Dangers of Electricity
Hazards:
Damaged insulation: contact with the wire (live wire especially) due to gap in the insulation causes electric shock which can cause serious injury or shock.
Overheating of cables: when long extension leads are coiled up, they may overheat. The current warms the wire, but the heat has less area to escape from a tight bundle. This might cause a fire.
Damp conditions: water can conduct a current, so if electrical equipment is wet someone might get electrocuted
Fuse:
A fuse protects a circuit.
Thin piece of wire which overheats and melts if current is too high.
It is placed on the live wire before the switch.
This prevents overheating and catching fire.
A fuse will have a specific current value (e.g. 13 Amps.) so when choosing a suitable fuse, you must use the one above minimum value but less than maximum value

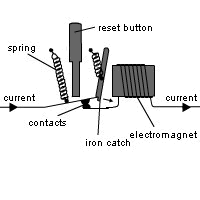
Circuit Breaker:
An automatic switch which if current rises over a specified value, the electromagnet pulls the contacts apart, breaking the circuit.
The reset button is to rest everything.
It works like a fuse but is better because it can be reset.
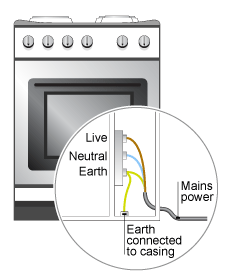
Benefits of Earthing a Metal Case:
Many electrical appliances, have metal cases, the earth wire creates a safe route for current to flow through if the live wire touches the casing
Earth terminal connected to metal casing, so in such a case, the current goes through earth wire instead of causing an electric shock.
A strong current surges through earth wire because it has very low resistance
This breaks the fuse and disconnects the appliance