Thermal Physics
Simple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter
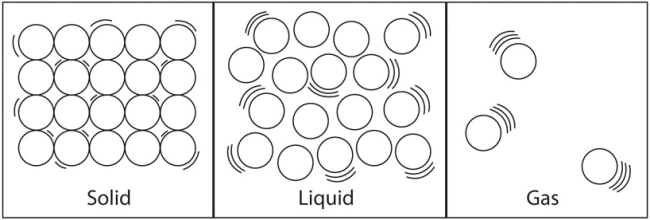
| Solid | Liquid | Gas |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed shape and volume | Fixed volume but changes shape depending on its container | No fixed shape or volume, gases fill up containers |
| Strong forces of attraction between particles- particles close to each other. | Weaker attractive forces than solids- medium distances between particels | Almost no intermolecular forces- large distances between particles |
| Fixed pattern (lattice) | No fixed pattern, liquids take shape of their container | Particles far apart, and move quickly |
| Atoms vibrate but can't change position fixed volume and shape | Particles slide past each other. |
The more the kinetic energy in a gas, the faster it's particles move and therefore the gas is at a higher temperature.
The pressure gases exert on a container is due to the particles colliding on the container walls.
The greater the kinetic energy in gasses the faster they move and the more often they collide on the container's walls.
Therefore, the volume is constant, then increasing the temperature will increase the pressure.
Thus, if there is a change in momentum of the particles, the kinetic energy decreases, decreasing the collisions on the container walls and thus the pressure.
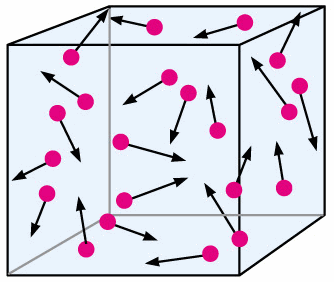
BROWNIAN MOTION
Gas molecules move randomly. This is because of repeated random collisions with other gas molecules, which constantly change the direction they move in.
Small molecules move much faster and have higher energy than larger molecules. They can effectively move large molecules due to repeated random bombardment- this can be seen by larger smoke particles moving.
Therefore, the random motion of particles in a suspension is evidence for the kinetic molecular model of matter.