General Physics
Length and Time
LENGTH
A rule (ruler) is used to measure length for distances between 1mm and 1meter.
For even smaller lengths, use a micrometer screw gauge.
SI unit for length is the meter (m)
To find out volume of regular object, use mathematical formula
To find out volume of irregular object, put object into measuring cylinder with water. When object added, it displaces water, making water level rise. Measure this rise. This is the volume.
TIME
Interval of time is measured using clocks or a stopwatch
SI unit for time is the second(s)
To find the amount of time it takes a pendulum to make a spin, time ~25 circles and then divide by the same number as the number of circles.
Motion
- Speed is the distance an object moves in a time frame. It is measured in meters/second (m/s) or kilometers/hour (km/h).
∴ Speedaverage=Total Distance Total Time∴ Speedaverage=Total Distance Total Time
Speed is a scalar quantity as it only shows magnitude.
Speed in a specified direction is velocity, which is a vector
SPEED TIME GRAPHS
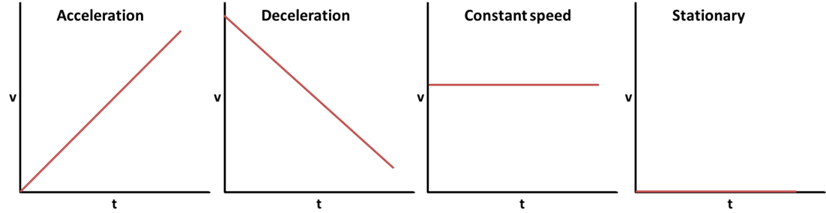
Area under the line equals to the distance travelled
Gradient=y2-y1x2-x1= ΔvtGradient=y2-y1x2-x1=Δvt = Acceleration (m/s)^2^
Positive acceleration means the velocity of a body is increasing
Deceleration or negative acceleration means the velocity of a body is decreasing
A curved speed time graph means changing acceleration.
Acceleration is the rate of change in velocity per unit of time, and a vector as it's direction is specified
DISTANCE TIME GRAPHS
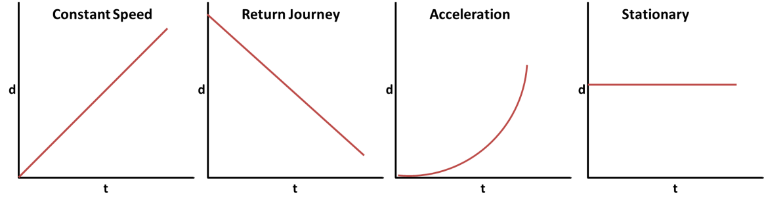
Gradient=y2-y1x2-x1=Δdt=Gradient=y2-y1x2-x1=Δdt= Speed (m/s)
Therefore, distance:
With constant speed: Speed × TimeSpeed×Time
With constant acceleration^1^: Final Speed+Initial Speed2×TimeFinalSpeed+InitialSpeed2×Time
ACCELERATION BY GRAVITY
An object in free-fall near to the Earth has a constant acceleration caused by gravity due to the Earth's uniform gravitational field
Objects are slowed down by air resistance. When deceleration caused by air resistance = acceleration by gravity, i.e. no net force acting on a body in free fall, the body reached terminal velocity
Mass and Weight
Mass: A measure of matter in a body and the body's resistance to motion.
Weight is the force of gravity on a body as a result of its mass.
Weight=Mass×GravityWeight=Mass×Gravity
- Weights (and hence masses) may be compared using a balance